First, their advertisement announces "free" services since it does not charge students, but SourceWatch indicates that this really isn't so. Taxpayers are footing the bill here with their hard-earned tax dollars and handing them over to Pearson, Inc., a private for-profit conglomerate : "Connections Education, that made an estimated $190 million in revenue in 2011." (see below) These are monies that are as a result NOT going into public education that consequently is party to the systematic undermining of public education.
Second, how is a parent supposed to know not only if this is a high performing academy, but also whether your child is better off going to this school than a brick and mortar one? And I'm not talking about understandable situations like in rural contexts that could, in some or many instances, benefit, but rather families like myself in an urban context that gets a mailer on it in the mail.
So if you look at the FAQs on their webpage on the TCA evaluation, here's what it says:
TCAH operates as an approved Houston Independent School District (HISD) campus charter and is accredited through HISD. Connections Academy is a division of Connections Education, which is accredited by AdvancED.AdvancED which accredits the school shows up as this non-descript website that you have to log into. It obviously can't or won't provide this information in the full light of day which smacks of un-professionalism, at best, and dishonesty, at worst.
They probably don't want the public to find out, among so many other things, just how poorly children in Connections Academy in Ohio fared where their schools failed to meet adequate yearly progress by LARGE margins. This doesn't matter for CA anyway because they still got their money—a whopping $19.2 million for a grand total of 3,123 students. What a sham and what a terrible disservice to the children and parents that fall prey to this nonsense.
Third, is the viability of establishing meaningful, interpersonal relationships online—especially when we know that these are vital to learning, socialization, and ultimately, mobility in school and life.
I agree with the recommendation that we cap growth of full-time charter schools. The for-profit motive together with the extant data are sufficiently troubling for this to be a hopeful direction for our nation's children.
-Angela
Connections Academy
 |
|
Find the privatizers and profiteers at OutsourcingAmericaExposed.org. |
 |
Learn more about corporations VOTING to rewrite our laws. |
The company's website says it provides "free" services since it does not charge students, but the services are far from free as they divert taxpayer dollars from the public school system to a private for-profit firm, Connections Education, that made an estimated $190 million in revenue in 2011.[1]
Connections Academy contracts with public school districts and charter schools to provide online classes for K-12 students.[2] Connections Academy had 21 schools and more than 27,000 students in the 2010-11 school year.[3] But some of those schools are failing. In September 2013, Politico reported that, "Ohio’s six biggest cyber schools all got Fs on their state progress reports, meaning students learned nowhere near a year’s worth of material in a year of studying online." Ohio Connections Academy received $19.2 million in taxpayer funds for 3,123 students, but those students are failing to meet adequate yearly progress by large margins (-11.3 in reading, -15.7 in math, -17.2 overall.)[4]
Connections Academy has ties to the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) and other organizations promoting a for-profit educational model from which it stands to benefit financially. Both on its own and as a member of ALEC, Connections Academy has pushed a national agenda to replace brick and mortar classrooms with computers and replace actual teachers with "virtual" teachers. Many have questioned the company's extraordinary revenues, generated at taxpayers' expense.[5] There has also been criticism of the quality of the teachers, the lack of government oversight and democratic accountability, as well as the appropriateness of taking children as young as five out of a classroom of their peers and putting them in front of a computer screen, according to the Washington Post.[6][7]
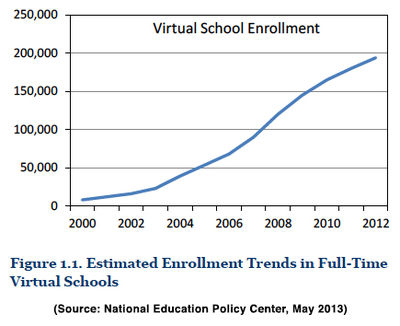
For many years, there was simply no data on virtual school performance. In 2012-13, state data became available indicating poor student achievement, as well as high student turnover, high student-teacher radios, uncertified teachers in some states (such as Florida),[8] and a funding formula that often gives companies extended periods of public funds for a child when the child may only stay at the cyber school for a brief period of time.[3] This new information has led some educators to call for a moratorium on the growth of full-time charter schools until policy-makers can assess the reasons for their significant failure to educate children.[9]
Contents
- 1 Data Shows that Cyber Schools Perform Significantly Worse than Brick and Mortar Schools
- 2 Low-Cost Education Yields High Profits and Poor Academic Outcomes
- 3 Other Controversies
- 3.1 Spending Taxpayer Dollars on Advertising to Pump Up Attendance Numbers and Taxpayer Subsidies
- 3.2 More than Double the "Churn" Rates of Brick-and-Mortar Schools in Arizona
- 3.3 Influencing Education in the States
- 3.4 Ties to the American Legislative Exchange Council
- 3.5 Ties to Jeb Bush's Foundation for Excellence in Education
- 4 "Risk Factors" in SEC filings
- 5 Political Activity
- 6 Personnel
- 7 Contact Information
- 8 Resources and Articles
PROFITS: According to Pearson's 2011 Annual Report, the company's share value increased by 20 percent in 2011 compared to the preceding year (before it acquired Connections Education), with revenues of over 5.8 billion British pounds, or more than $9.2 billion.[13][14] (Its adjusted operating profit for 2010 was 942 million British pounds, or $1.1 billion.)[15] In 2012, Pearson took in 6.1 billion British pounds (about $9.7 billion) in revenues, with an adjusted operating profit of 936 million British pounds (approximately $1.5 billion).[16][17]
BUSINESS MODEL: Connections Academy currently operates tuition-free online "public schools" under management contracts from charter schools or school districts in Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Texas, Utah, Wisconsin, and Wyoming in 2013, according to the company's website.[2]
Data Shows that Cyber Schools Perform Significantly Worse than Brick and Mortar Schools
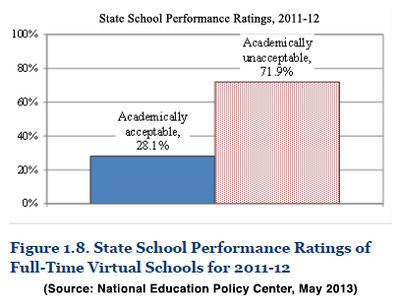
In recent years, there has been an explosion of virtual schools (also called internet schools, cyber schools, and online schools). From 2008 to 2012, 157 bills passed in 39 states and territories (including the District of Columbia) that expand online schooling, regulate virtual education, or modify existing regulations, according to a National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) database.[18] Many of these bills are attributable to American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) politicians. As discussed below, ALEC passed a "model" virtual schools act in 2004.Until recently, data on performance was scarce, but educators at the National Education Policy Center (NEPC) did two of the first empirical studies in 2012 and 2013 on the effectiveness of full-time online schools. The authors concluded that despite the amount of taxpayer dollars going towards these schools, there is "very little solid evidence to justify the rapid expansion of virtual education." One of the studies, looking at state data on performance, shows major problems with cyber schools. The 2013 report by NEPC notes, "on the common metrics of Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP), state performance rankings, and graduation rates, full-time virtual schools lag significantly behind traditional brick-and-mortar schools."[3]
In the 2010-2011 school year, only 23.6 percent of virtual schools met AYP standards, whereas 52 percent of brick-and-mortar public school districts and charter schools met the same progress standards.[3] According to another (2012) report by NEPC, "Among the large-sized EMOs, those companies with the lowest proportion of schools meeting AYP are White Hat Management (7 percent), Charter Schools USA (10 percent), Educational Services of America Inc. (10 percent), Connections Academy (27 percent), Academica (29 percent), and K12 Inc. (33 percent)" (emphasis added).[19]
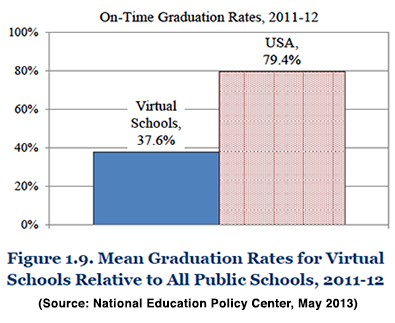
The same study also shows that on-time graduation rates are much lower on average at online schools than at all public schools in the United States: only 37.6 percent of students at virtual high schools graduate on time, whereas the national average for all public high schools is 79.4 percent, more than twice that.[3] Other critics have wondered where some of the taxpayer dollars directed to online schools end up.
A September 2013 Politico investigation of Ohio virtual schools found that, of the six biggest online schools in the state, they all received "failing grades" from the Ohio Department of Education for academic performance. Ohio Connections Academy received $19.2 million in taxpayer funds for 3,123 students, but those students are failing to meet adequate yearly progress by large margins (-11.3 in reading, -15.7 in math, -17.2 overall.)[20]
A study of the performance of Pennsylvania online charter schools by the Center for Research on Education Outcomes (CREDO) at Stanford University in 2011 found that 100 percent of cyber charters performed "significantly worse than their traditional public school counterparts in both reading and math.”[21]
A ten-month investigation of Colorado virtual schools found that half of the students of online schools left within a year, and that when they returned to brick-and-mortar schools they were often further behind academically than when they started.[22]
Low-Cost Education Yields High Profits and Poor Academic Outcomes
Connections Academy saves money by not having buildings, classrooms, books, etc., and also cuts costs by reducing curriculum and teachers, according to the New York Times.[1] During a presentation at the Virginia legislature in 2011, a representative of Connections Academy explained that its services were available at three price points per student:- "Option A: $7,500, a student-teacher ratio of 35-40 to 1, and an average teacher salary of $45,000.
- "Option B: $6,500, a student-teacher ratio of 50 to 1, with less experienced teachers paid $40,000.
- "Option C: $4,800 and a student-teacher ratio of 60 to 1, as well as a narrower curriculum."[1]
- "Despite lower operating costs, the online companies collect nearly as much taxpayer money in some states as brick-and-mortar charter schools. In Pennsylvania, about 30,000 students are enrolled in online schools at an average cost of about $10,000 per student. The state auditor general, Jack Wagner, said that is double or more what it costs the companies to educate those children online."[1]
Other Controversies
Spending Taxpayer Dollars on Advertising to Pump Up Attendance Numbers and Taxpayer Subsidies
A 2012 article in USA Today revealed that 10 of the biggest for-profit online K-12 schools (including Connections, which is the second largest) "have spent millions in taxpayer dollars on advertising" -- $94.4 million from 2007 to 2012.[24]
Jim Buckheit, executive director of the Pennsylvania Association of School Administrators, told the New York Times, "Some of the cyber charter schools have fairly aggressive recruitment campaigns. . . . They have vans, billboards, TV and radio ads. They set up recruitment meetings in area hotels and invite parents to come."[1]
The massive advertising pulls in parents, students, and state money, but students often do not stay in the cyber school, and one study indicates that "churn" -- or turnover -- of students could be more than 50 percent in some schools.[3]
More than Double the "Churn" Rates of Brick-and-Mortar Schools in Arizona
Arizona Connections Academy has "reported that 30 percent of enrolled students leave sometime during the school year," according to the Arizona Republic. In comparison, Mesa Unified, the school's largest district, had a "churn" rate of 12 percent in the 2010-2011 school year. The Arizona Republic report added that "doubts about quality plague Arizona's online schools," and "the largest online schools in K-12 lag the state averages among all Arizona public schools in most standardized test scores and in graduation rates. Turnover of students is high, which indicates many students have failed to get traction in mastering their courses or maintaining their motivation."[25]Influencing Education in the States
Connections Academy has sought to dramatically change the face of state-level education policy to favor its for-profit education agenda, sometimes with the help of ALEC and the Foundation for Excellence in Education (see more about FEE below). Below are some examples where the firm has succeeded in diverting public funds to private for-profit education:Maine
In Maine, Governor Paul LePage has worked closely with national virtual school lobbying groups to craft Maine's education policy.[26] Connections Academy has hired former Maine State Chamber of Commerce lobbyist and GOP legislative staffer Chris Jackson[27] to lobby for the company in 2011 and 2013, according to the Maine Commission on Governmental Ethics and Election Practices.[28][29]Governor LePage, whose administration has put a priority on subsidizing for-profit education corporations with public funds, named Stephen Bowen as Commissioner of the Maine Department of Education in 2011. Bowen was a member of the ALEC Education Task Force when he worked on the staff of the Maine Heritage Policy Center, a member of the right-wing web of groups called the State Policy Network.[30] In January 2013, LePage called for the resignation of Maine Charter School Commission members who turned down four out of five charter school applications, including a repeat attempt by K12 Inc. and Connections Academy.[26]
Wisconsin
In March 2011, Rep. Robin Vos, former ALEC state chairman for Wisconsin, introduced Assembly Bill 51, which was to erase the cap on the number of pupils who may attend virtual charter schools and weaken teacher licensing requirements.[5] AB 51 drew from a number of ALEC bills, especially the "Next Generation Charter Schools Act," which includes the idea of an authorizing board that makes it easier to establish charter schools over the objections of school districts and other school officials, and the "Charter Schools Act," which states that charter schools are to be funded at a per-pupil rate, as public schools are.[5]On February 10, 2011, Thomas Fonfara of Arrowhead Strategies, LLC registered as a lobbyist on behalf of Connections Academy/Connections Education LLC. Between that date and June 30, 2011, Connections paid him $24,000[31] for "development, drafting or introduction of a proposal relating to virtual charter schools" or "virtual schools," intending to affect "both legislative matter and rule," according to the Wisconsin Government Accountability Board.[32]
Connections Academy was a private sector chair of the ALEC Education Task Force at the time the Charter School Reform Bill (AB 51-SB 22) was introduced and stood to benefit from its passage through its Wisconsin Connections Academy.[5] When the bill failed to pass, Governor Scott Walker instead added a provision to the state budget to lift the enrollment cap on virtual charter schools, while the budget simultaneously stripped $834 million from Wisconsin public schools.[33]
Connections had previously hired Thomas Fonfara to lobby on its behalf from 2006 to 2008.[34] In January 2008, the Wisconsin state legislature introduced AB 697 and SB 396 relating to "virtual charter schools" and "online courses for elementary and secondary school pupils and granting rule-making authority."[35][36] In the first half of 2008, Connections Academy spent over $35,000 in lobbying expenditures to Fonfara and his firm at the time, Quarles & Brady, lobbying on these two bills and another related virtual schools bill.[37] SB 396, a compromise bill to keep Wisconsin's virtual schools open after an appeals court ruled that the largest virtual school in the state had violated state law,[38] was signed by Governor Jim Doyle on April 7, 2008,[35] and became the 2007 Wisconsin Act 222.
Ties to the American Legislative Exchange Council
Connections Academy was a long-time member of the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC). Mickey Revenaugh, Connections Academy co-founder and Executive Vice President of Sales and Marketing at the Connections Learning division under Pearson, was the co-chair of ALEC's Education Task Force as of May 2012.[39][40][41] Connections Academy was heavily involved in ALEC's model bill, the "Virtual Public Schools Act," which makes online schools recognized public schools, meaning they must be given the same resources and funding as other public schools in that state (see below for more).| About ALEC |
|---|
|
ALEC
is a corporate bill mill. It is not just a lobby or a front group; it
is much more powerful than that. Through ALEC, corporations hand state
legislators their wishlists to benefit their bottom line. Corporations
fund almost all of ALEC's operations. They pay for a seat on ALEC task
forces where corporate lobbyists and special interest reps vote with
elected officials to approve “model” bills. Learn more at the Center for
Media and Democracy's ALECexposed.org, and check out breaking news on our PRWatch.org site.
|
ALEC bills benefiting Connections Academy are still moving across the country, however. At least 139 bills promoting a private, for-profit education model were introduced in 43 states and the District of Columbia in the first half of 2013, and 31 became law, according to "ALEC at 40: Turning Back the Clock on Prosperity and Progress," an August 2013 report by the Center for Media and Democracy (CMD).[43]
Virtual Public Schools Act
ALEC and K12 Inc. work together to cash in on kids
In 2004 when the "model" bill was drafted and approved, both Connections Academy and K12 Inc. were part of the "School Choice Subcommittee" of ALEC's Education Task Force, according to an archived version of ALEC's website from February 2005. The subcommittee recommended six bills for adoption, including the "Virtual Public Schools Act." According to ALEC, the bill was drafted by Mickey Revenaugh of Connections Academy along with Bryan Flood of K12 Inc., then-Colorado Representative Don Lee (now a lobbyist for K12 Inc.), "and the rest of the Subcommittee."[45]
The bill was approved at a closed-door meeting of the ALEC Education Task Force in December 2004 and became model legislation in January 2005, when ratified by ALEC's Board of Directors.[46]
The "Virtual Public Schools Act" is still moving in 2013. Between January and August 2013, state bills similar to ALEC's "model" were introduced in Arizona and Maine and passed in Michigan (HB 4228), according to CMD's report on ALEC bills in 2013.[43]
Previous to 2013, the bill was introduced in at least Mississippi, Maine, Tennessee, Massachusetts, Virginia, and Texas, according to a September 2012 report by In the Public Interest (ITPI). The bill paved "the way for corporations to offer virtual online classes to public school students. In many of these states, legislators that sponsored this legislation were members of ALEC," according to ITPI, which describes itself as "a comprehensive resource center on privatization and responsible contracting."[47]
The legislation offers enormous opportunities for the corporations that promoted it with the help of ALEC. In the states that have passed the model bill, these companies have strong operations. Connections Academy runs a virtual public school in Texas and has schools under development in Tennessee and Virginia.[48]
Parent Trigger Act
"Won't Back Down" misleadingly portrays
"Parent Trigger" laws as an effective mechanism for transforming
underperforming public schools
Ties to Jeb Bush's Foundation for Excellence in Education
Connections Academy has funded the Foundation for Excellence in Education (FEE), a non-profit education reform advocacy group founded by former Florida governor Jeb Bush, according to emails released by the non-profit privatization resource organization In the Public Interest.[51] FEE is "backed by many of the same for-profit school corporations that have funded ALEC and vote as equals with its legislators on templates to change laws governing America's public schools," as noted by PRWatch. Bush's group is also "bankrolled by many of the same hard-right foundations bent on privatizing public schools that have funded ALEC" and "they have pushed many of the same changes to the law, which benefit their corporate benefactors and satisfy the free market fundamentalism of the billionaires whose tax-deductible charities underwrite the agenda of these two groups."[13]As In the Public Interest reports, e-mails between FEE and conservative state education officials in Florida, New Mexico, Maine, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, and Louisiana show that the foundation is writing state education laws and regulations in ways that could benefit its corporate funders:
- "The emails, obtained through public records requests, reveal that the organization, sometimes working through its Chiefs For Change affiliate, wrote and edited laws, regulations and executive orders, often in ways that improved profit opportunities for the organization’s financial backers. Bush has been referred to as the 'godfather' of Chiefs for Change, an alliance of conservative state superintendents and education department directors with significant authority over purchasing and policy in their states."[52]
"Risk Factors" in SEC filings
In its U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filings, publicly traded companies are required to highlight for shareholders any “risk factors” in their sector that could affect their business and future prospects. These risk factors, which are listed in the annual report (Form 10-K) often show the incentives the company has to influence public policy and the direction their advocacy would take.As a privately held company, Connections Education (parent corporation of Connections Academy) has no obligation to file a 10-K form with the federal government. However, its owner, UK-based Pearson, has an annual report that is publicly available. In its latest report, Pearson cites "education regulation and funding" as principal risks, high in both probability and impact, that may adversely affect its "business strategy, financial position or future performance."[15] With regard to education regulation and government funding of its United States operations, Pearson states:
- "In the US we actively monitor changes through participation in advisory boards and representation on standard setting committees. . . . We work through our own government relations team . . . [to monitor] municipal funding and the impact on our education receivables."[16]
Political Activity
Connections Education has spent $270,000 on education lobbying at the federal level from 2009 to 2011: $60,000 in 2009 (as Connections Academy), $120,000 in 2010, and $90,000 in 2011.[53]At the state level, Connections Education registered lobbyists in nine states from 2010 through 2012, the three years since it was founded,[54] while Connections Academy and its state-based affiliates have lobbied in 27 states from 2003 through 2012.[55] In Wisconsin alone, Connections Academy has spent over $92,000 lobbying on the issue of virtual public schools, according to a review of Wisconsin Government Accountability Board data by the Center for Media and Democracy.[56]
In 2011, the progressive group Our Oregon reported that freshman Oregon State Rep. Matt Wingard (R-Wilsonville), a vocal advocate of online schools and Connections Academy in particular, was actually on the payroll of Connections Academy while in public office in at least 2008.[57] It also noted that the President of Oregon Connections Academy is Jeff Kropf, former state legislator and later state director of the Koch-funded Americans for Prosperity.[58]
Personnel
Chief Executive Officer
Barbara Dreyer is a Connections Academy co-founder (with Mickey Revenaugh) and currently its Chief Executive Officer and President. Information about her compensation is not available as of September 2013. She previously founded two technology companies: Speakout.com/Ntercept Communications, a web research group that existed from 1999 to 2002, of which she was also Chief Operating Officer;[59] and VideoGrafects, a multimedia development company, of which she was also President.[60][61] She also has previous experience in accounting as well as in telecommunications, venture capital, and chemical manufacturing firms, but no known previous experience in education.[62]Management Team
As of July 2013:[63]- Barbara Dreyer - President and CEO
- Dr. Patricia Hoge, Senior Vice President Curriculum and Instruction and Chief Academic Officer
- Ted Ochs, Chief Operations Officer and Chief Financial Officer
- Marc Guerrasio, Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer
- Susan Fancher, Senior Vice President, Marketing
- Monte Kalisch, Senior Vice President, Development
- Yvonne Kisiel, Senior Vice President and General Counsel
- Pat Laystrom, Senior Vice President, State Relations
- Deane Turner, Senior Vice President, Operations
- Earl W. Grier, Jr., Vice President of Schools
- Dr. Donna Hutchison, Vice President, State Relations
- Robert D. Pouliot, Vice President of Operations
- Peter Robertson, Vice President of Schools
- David Schmidt, Vice President, State Relations
- Susan Stagner, Vice President State Relations
- Dr. Steven Guttentag - Executive Vice President and Chief Education Officer (current President of Connections Learning)
- Mickey Revenaugh - Senior Vice President, State Relations (current Executive Vice President of Sales and Marketing at Connections Learning)
Contact Information
Corporate Headquarters:1001 Fleet Street, 5th Floor
Baltimore, MD 21202
Phone: (443) 529-1000
Web: http://www.connectionsacademy.com
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/ConnectionsAcademy
Twitter: @ConnectionsAcad
Resources and Articles
Key Studies
- Stephanie Simon, Cyber schools flunk, but tax money keeps flowing, Politico, September 25, 2013.
- Alex Molnar, Ed., National Education Policy Center, Virtual Schools in the U.S. 2013: Politics, Performance, Policy, and Research Evidence, organizational report, May 2013.
- Center for Public Education, Searching for the Reality of Virtual Schools, organizational report, May 2012.
- Stephanie Saul, Profits and Questions at Online Charter Schools, New York Times, December 12, 2011.
- Lee Fang, How Online Learning Companies Bought America's Schools, The Nation, December 5, 2011.
- Gene V. Glass and Kevin G. Welner, National Education Policy Center, Online K-12 Schooling in the U.S.: Uncertain Private Ventures in Need of Public Regulation, organizational report, October 2011.
- Burt Hubbard and Nancy Mitchell, Online K-12 Schools Failing Students but Keeping Tax Dollars, iNews Network (Rocky Mountain PBS), September 27, 2011.
- Julie Underwood, ALEC Exposed: Starving Public Schools (sub. req'd.), The Nation, July 12, 2011.
- Center for Research on Education Outcomes, Charter School Performance in Pennsylvania, organizational report, April 4, 2011.
Related SourceWatch Articles
- K12 Inc.
- Outsourcing America Exposed Portal
- American Legislative Exchange Council
- Foundation for Excellence in Education
Related PRWatch Articles
- Mary Bottari, From Junk Bonds to Junk Schools: Cyber Schools Fleece Taxpayers for Phantom Students and Failing Grades, PRWatch, October 2, 2013.
- Brendan Fischer, Cashing in on Kids: 139 ALEC Bills in 2013 Promote a Private, For-Profit Education Model, PRWatch, July 16, 2013.
- Lisa Graves, "Taxpayer-Enriched Companies Back Jeb Bush's Foundation for Excellence in Education, its Buddy ALEC, and Their 'Reforms,'" PRWatch, November 28, 2012.
- Mary Bottari and Sara Jerving, "Won't Back Down" Film Pushes ALEC Parent Trigger Proposal, PRWatch, September 19, 2012.
- Rebekah Wilce, EnergySolutions and Connections Education Are 27th and 28th Corporations to Leave ALEC, PRWatch, July 20, 2012.
- Dustin Beilke, ALEC Education "Academy" Launches on Island Resort, PRWatch, February 2, 2012.
- Mary Bottari, ALEC Bills in Wisconsin, PRWatch, July 14, 2011.
External Articles
- Sean Cavanagh, N.M. Schools Chief Overrules Panel, Clears Path for Virtual School, Education Week, February 5, 2013.
- Valerie Strauss, E-mails link Bush foundation, corporations and education officials, Washington Post, January 30, 2013.
- Stephanie Simon, "Online schools face backlash as states question results," Reuters, October 3, 2012.
- Forces behind the privatization of education, Workers World, May 17, 2012.
- Rhania Khalek, Why Is Public Education Being Outsourced to Online Charter Schools?, Alternet, January 8, 2012.
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Stephanie Saul, Profits and Questions at Online Charter Schools, New York Times, December 12, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Connections Academy About Connections Academy, a Free Online School, company website, accessed July 2013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 National Education Policy Center, Virtual Schools in the U.S. 2013: Politics, Performance, Policy, and Research Evidence, organizational report, Alex Molnar, ed., May 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Politico, Cyber schools flunk, but tax money keeps flowing, September 25, 2013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Mary Bottari, ALEC Bills in Wisconsin, PRWatch, July 14, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Lyndsey Layton, Study raises questions about virtual schools, Washington Post, October 24, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Lyndsey Layton and Emma Brown, Virtual schools are multiplying, but some question their educational value, Washington Post, November 26, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Trevor Aaronson and John O'Connor, Florida Investigates K12, Nation's Largest Online Educator, State Impact (NPR), September 11, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ National Education Policy Center, A Study of Student Characteristics, School Finance, and School Performance in Schools Operated by K12 Inc., organizational report, July 2012.
- Jump up ↑ Dun & Bradstreet, "Apollo Management, L.P. Report," online business credit report, prepared June 15, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Connections Education, Connections Education, organizational website, accessed July 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Pearson, Pearson acquires Connections Education, corporate press release, September 15, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 13.0 13.1 Lisa Graves, "Taxpayer-Enriched Companies Back Jeb Bush's Foundation for Excellence in Education, its Buddy ALEC, and Their 'Reforms,'" PRWatch, November 28, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ X-Rates, Rate US Dollar per 1 British Pound Monthly average 2011, currency exchange rate website, accessed July 2013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 15.0 15.1 Pearson, Annual Report and Accounts, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 Pearson, Annual Report and Accounts, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ X-Rates, Rate US Dollar per 1 British Pound Monthly average 2012, currency exchange rate website, accessed July 2013.
- Jump up ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, Education Bill Tracking Database, organizational database, accessed September 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Gary Miron, Jessica Urschel, Mayra A. Yat Aguilar, Breanna Dailey, National Education Policy Center, Profiles of For-Profit and Nonprofit Education Management Organizations: Thirteenth Annual Report - 2010-2011, organizational report, January 6, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ Politico, Cyber schools flunk, but tax money keeps flowing, September 25, 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Center for Research on Education Outcomes, Charter School Performance in Pennsylvania, organizational report, April 4, 2011, p. 20.
- Jump up ↑ Burt Hubbard and Nancy Mitchell, Online K-12 Schools Failing Students but Keeping Tax Dollars, iNews Network (Rocky Mountain PBS), September 27, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Eric Litke, Virtual schools offer cost savings, Manitowoc Herald Times Reporter, August 27, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ Greg Toppo, Online schools spend millions to attract students, USA Today, November 28, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ Pat Kossan, Anne Ryman, and Matt Dempsey, Online schools face questions over quality, effectiveness, Arizona Republic, December 11, 2011.
- ↑ Jump up to: 26.0 26.1 Andy O’Brien, A Virtual Impasse in Augusta on Charter Schools, The Free Press, July 3, 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Federle Mahoney Government Affairs, LLC, Chris Jackson, lobbying firm biography, accessed September 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Maine Commission on Governmental Ethics and Election Practices, Lobbyist Compensation 2013, state lobbyist compensation spreadsheet, file last updated July 24, 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Maine Commission on Governmental Ethics and Election Practices, Lobbyist Compensation Report 2011, state lobbyist compensation spreadsheet, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ American Legislative Exchange Council, Education Task Force Director, organizational document, July 1, 2011, document obtained and released by Common Cause.
- Jump up ↑ Wisconsin Government Accountability Board, Lobbying and Time Expenditures: Connections Education LLC, Eye on Lobbying state lobbying database, January 1 - June 30, 2011 report.
- Jump up ↑ Wisconsin Government Accountability Board, Lobbying Principals: Connections Education LLC: Interests, Eye on Lobbying state lobbying database, reporting date January 1, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Amy Hetzner and Erin Richards, Budget cuts $834 million from schools, Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, March 1, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ National Institute on Money in State Politics, Client Summary: Connections Academy Inc., FollowTheMoney state political influence database, accessed September 2013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 35.0 35.1 Wisconsin State Legislature, SB 396, state legislative bill tracking website, accessed September 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Wisconsin State Legislature, AB 697, state legislative bill tracking website, accessed September 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Wisconsin Government Accountability Board, Lobbying and Time Expenditures: Connections Academy Inc, Eye on Lobbying state lobbying database, January 1 - June 30, 2008.
- Jump up ↑ Kathy Walsh Nufer, Compromise good news for state's virtual schools (sub. req'd.), Appleton Post-Crescent (accessed via Lexis-Nexis), March 12, 2008.
- Jump up ↑ Pearson, Connections Learning division, Management Team: Mickey Revenaugh, corporate website, accessed September 2013.
- Jump up ↑ American Legislative Exchange Council, Education Task Force, organizational website, accessed July 8, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ American Legislative Exchange Council, Education Task Force Meeting Agenda, organizational agenda, May 11, 2012, document obtained and released by Common Cause.
- Jump up ↑ Rebekah Wilce, EnergySolutions and Connections Education are 27th and 28th Corporations to Leave ALEC, PRWatch.org, July 20, 2012
- ↑ Jump up to: 43.0 43.1 43.2 Center for Media and Democracy, ALEC at 40: Turning Back the Clock on Prosperity and Progress, organizational report, August 2013, p. 25.
- Jump up ↑ Lisa Graves, Taxpayer-Enriched Companies Back Jeb Bush's Foundation for Excellence in Education, its Buddy ALEC, and Their "Reforms", PRWatch, November 28, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ American Legislative Exchange Council, Education Task Force: News: Task Force Meeting December 4, 2004, organizational website, archived by the Wayback Machine on February 4, 2005.
- Jump up ↑ American Legislative Exchange Council, Virtual Public Schools Act, organizational "model" legislation, approved January 2005, obtained and released by the Center for Media and Democracy July 2011, accessed September 2013.
- Jump up ↑ In the Public Interest, Profiting from Public Dollars: How ALEC and Its Members Promote Privatization of Government Services and Assets, September 2012.
- Jump up ↑ Connections Academy, About Us, company website, accessed September 2013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 49.0 49.1 American Legislative Exchange Council, ALEC Education Task Force 35-Day Mailing, organizational document, March 31, 2011, obtained and released by Common Cause April 2012.
- ↑ Jump up to: 50.0 50.1 Mary Bottari and Sara Jerving, "Won't Back Down' Film Pushes ALEC Parent Trigger Proposal," PRWatch, September 19, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ In the Public Interest, Corporate Interests Pay to Play to Shape Education Policy, Reap profits: Emails Show Bush-Led Organization's ALEC-Like Role in State Policymaking, organizational publication, January 30, 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Donald Cohen, In the Public Interest, Bush's Education Nonprofit and Corporate Profits, organizational publication, January 30, 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Center for Responsive Politics, Lobbying: Connections Education (Summary), OpenSecrets lobbying database, accessed July 2013.
- Jump up ↑ National Institute on Money in State Politics, Connections Education, FollowTheMoney.org state lobbying database, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ National Institute on Money in State Politics, Connections Academy, FollowTheMoney.org state lobbying database, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Wisconsin Government Accountability Board, Lobbying Principals, Eye on Lobbying database, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Rep. Matt Wingard, 2009 Annual Verified Statement of Economic Interest, Oregon state ethics disclosure, April 6, 2009.
- Jump up ↑ Scott Moore, Matt Wingard's Plan to Line His Pockets with Your Tax Dollars, Our Oregon, June, 2011.
- Jump up ↑ Ntercept Communications, Bloomberg BusinessWeek, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Barbara Dreyer, LinkedIn.com profile, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ University of Maryland University College, Dreyer, academic biography, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Connections Academy, Barbara Dreyer, corporate biography, accessed August 2013.
- Jump up ↑ Connections Academy, Management Team, organizational website, accessed July 2013.

No comments:
Post a Comment